TECHNICAL MONITORING
Technical monitoring in geotechnical engineering refers to the systematic observation of the behavior of soil, structures, and the surrounding area during all phases of a project – from the conceptual design to the use of the structure.
Its purpose is the timely detection of changes that could affect the stability, safety, or durability of the structure, as well as enabling decision-making based on actual data.
Pored sigurnosnih aspekata, pravilna procjena tla značajno utječe na ekonomičnost projekta. Pravovremeno prepoznavanje mogućih izazova omogućuje projektantima da predvide potrebne zahvate i smanje nepredviđene troškove tijekom gradnje. Na primjer, ako se ustanovi da tlo ima nisku nosivost, moguće je unaprijed planirati dodatne mjere stabilizacije, čime se izbjegavaju kasnije sanacije i dodatni radovi.
Osim same gradnje, detaljna analiza tla važna je i za zaštitu okolnih objekata i infrastrukture. Svaka intervencija na terenu može utjecati na susjedne građevine, pa je važno predvidjeti moguće promjene i spriječiti negativne posljedice.
Zbog svega navedenog, stručna procjena podloge nezaobilazan je korak u svakom građevinskom projektu. Kvalitetno planiranje i izvođenje radova temeljenih na preciznim podacima osigurava sigurnost, dugotrajnost i ekonomičnost građevina, čime se izbjegavaju nepredviđeni problemi i dodatni troškovi u budućnosti.
Planning and design of technical monitoring systems
Before the start of construction works, a monitoring plan is developed, tailored to the type of structure and site conditions. The investor’s requirements, design documentation, and site-specific characteristics are taken into account. Appropriate measuring equipment is selected, installation locations are determined, and the frequency and duration of monitoring are defined.
Installation and configuration of equipment
Depending on the project, devices are installed to measure displacements, inclinations, deformations, or other relevant parameters. For example, a vertical inclinometer is used to monitor horizontal movements of soil or structures at different depths. Installation is carried out in accordance with technical specifications, and the system is tested before the start of measurements.
Measurement implementation
Measurements are carried out at predefined intervals, which may vary depending on the construction phase and the type of structure. The procedures include initial (baseline) measurements, comparisons with subsequent readings, and trend analysis. In inclinometer measurements, a probe is used to record angular deviations in two planes, and the results are processed using specialized software.
SMGE Studio currently provides technical monitoring services in the form of measuring horizontal displacement using a vertical inclinometer.
SMGE studio trenutno pruža uslugu tehničkog promatranja u vidu mjerenja horizontalnog pomaka na vertikalnom inklinometru.SMGE Studio currently provides technical monitoring services in the form of horizontal displacement measurements using a vertical inclinometer.
Vertical Inclinometer
Definition
– A vertical inclinometer is a geotechnical measuring device installed in a vertical borehole, which uses sensors to record angular deviations from the vertical. By analysing this data by depth, horizontal ground or structural displacements are determined to monitor the stability of the terrain and structures.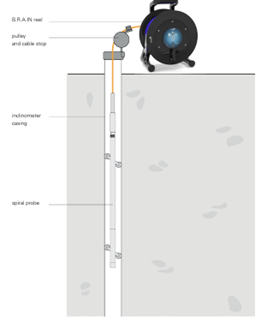
The trial measurement equipment consists of the following:
- Inclinometer probe
- Measuring cable with winding reel
- Mobile device
- B.R.A.IN mobile application for reading and storing measurement data
The measuring equipment consists of the following:
- Replacement probe without sensors
- Cable with winding reel (same reel is used)



Measurement execution
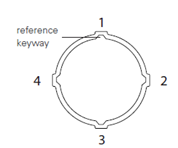
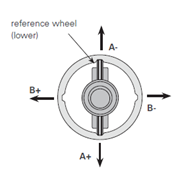
When taking measurements with an inclinometer probe, two passes are carried out: an initial measurement and a measurement rotated by π (180°), in order to minimize errors during inclinometer probe readings. The directions of positive inclination readings of the inclinometer probe are shown in the figure below.
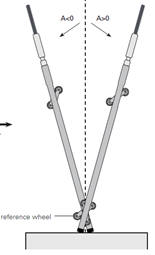

Measurement procedure:
1. Use the trial probe to check the accessibility and length of the inclinometer installation, and adjust future measurements accordingly.
2. Perform measurements in at least two planes A1B1–A3B3 (0° and 180°).
3. Before taking the actual measurement at the bottom of the borehole, wait 5–10 minutes to allow the probe to stabilize.
4. Carry out a reference measurement (“0” measurement) – all future displacements will be compared to this reference measurement.
5. Perform measurements according to the measurement program, in accordance with the project documentation or as agreed with the Supervising Engineer.
2. Perform measurements in at least two planes A1B1–A3B3 (0° and 180°).
3. Before taking the actual measurement at the bottom of the borehole, wait 5–10 minutes to allow the probe to stabilize.
4. Carry out a reference measurement (“0” measurement) – all future displacements will be compared to this reference measurement.
5. Perform measurements according to the measurement program, in accordance with the project documentation or as agreed with the Supervising Engineer.
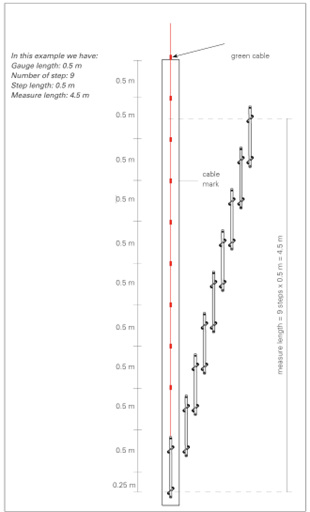
Measurement frequency
The frequency of measurements is defined with respect to the excavation depth of the construction pit and the calculated displacements specified in the project. The purpose of monitoring is to confirm the design assumptions as well as to enable timely interventions in case of larger-than-expected movements. A further and more detailed measurement program can be agreed upon in cooperation with the Client, Designer, or Supervising Engineer, depending on the situation on site.
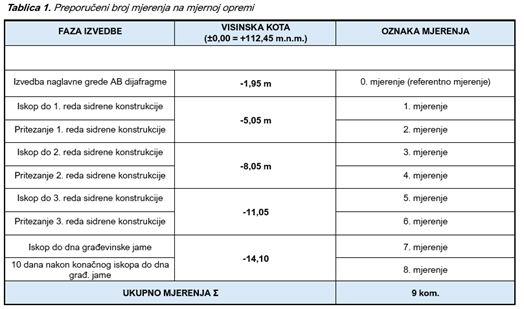
In general, the frequency of measurements on the monitoring equipment can be as follows (example given for a temporary construction pit):
In general, the frequency of measurements on the monitoring equipment can be as follows (example given for a temporary construction pit):
Data processing
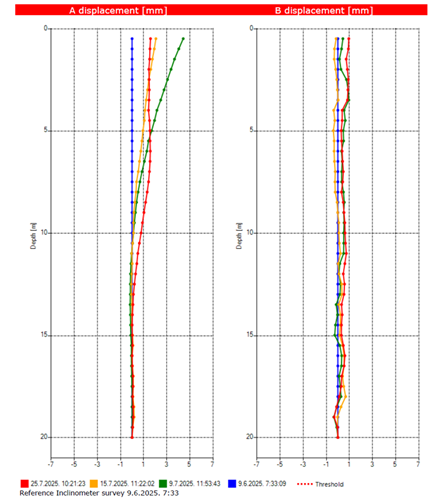
The processing of measurement data is carried out using the KLION v1.5.3 software by SISGEO S.R.L.
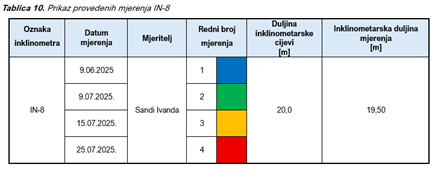
Below are some of the results obtained during the technical monitoring of a temporary excavation pit with a reinforced concrete diaphragm wall structure. The first measurement, numbered as 1, is also referred to as the “0” measurement (reference measurement).
ENTRUST YOUR PROJECT TO OUR TEAM.
Ready for a safe and high-quality start to your project? Contact us, and together, we will find the best solution for your site.
